Why was the Kahramanmaras earthquake so devastating?
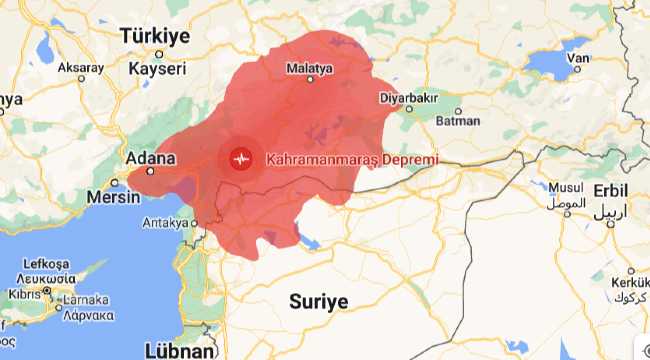
According to seismologists the earthquakes that occurred in Kahramanmaraş were among the most widespread earthquakes in the history of the region because they caused a crack of more than 100 kilometers extending to Anatolia and the Arabian peninsula.
WHAT CAUSED THE EARTHQUAKE ?
The Earth’s crust consists of intertwined but actually separate parts called ”plates”. These plates often try to move, but cannot do so as a result of the pressure of other parts touching each other. But sometimes the pressure on one of these plates accumulates, and then this pressure rises to the surface as energy. This energy moves the surface; that is, it creates an earthquake. In the last event, the Arabian plate moved towards the north and put pressure on the Anatolian plate.
The thrust force and pressure between these plates had also led to very serious decays in the past. On August 13, 1822, a magnitude 7.4 earthquake had occurred in the same region on the same fault line. 7 Thousand people had in Aleppo alone; about 20 thousand people had lost their lives in total.
WHY WERE THE EARTHQUAKES SO POWERFUL?
The Eastern Anatolia Fault line is a fault line with a “straight line pulse”. In this type of fault lines, hard rock blocks exert pressure on each other on a vertical line, and eventually a block that cannot withstand the pressure moves horizontally. This creates such a tension that an earthquake occurs.
In the Kahramanmaraş earthquake, this fracture occurred in a place that was not very deep. Geophysics experts say “The closer an earthquake of the same magnitude gets to the surface, the bigger the impact.”
BUILDINGS WERE NOT DURABLE
On the other hand the fact that the buildings were not durable enough most obviously had an impact on the loss of many lives.
FAULT FRAGMENTS THAT ACCUMULATED FOR 500 YEARS BROKE
Regarding the 7.4 magnitude earthquake that shook Turkey, a geological engineer and professor at the Earthquake Research and Application Center of “Izmir Dokuz Eylul University” said, “In the region where today’s earthquake occurred, fault fragments that accumulated stress for 500 years broke. Since the earthquake generation period of these faults is also 400-500 years, earthquakes were expected on these faults in a scientific sense. The earthquake that occurred today must have occurred as a result of the fracture of the fault fragments between Malatya and Hatay on the southern branches of the Eastern Anatolian fault.” (bbc.com/turkce/articles/c3gnez8eq9qo)





